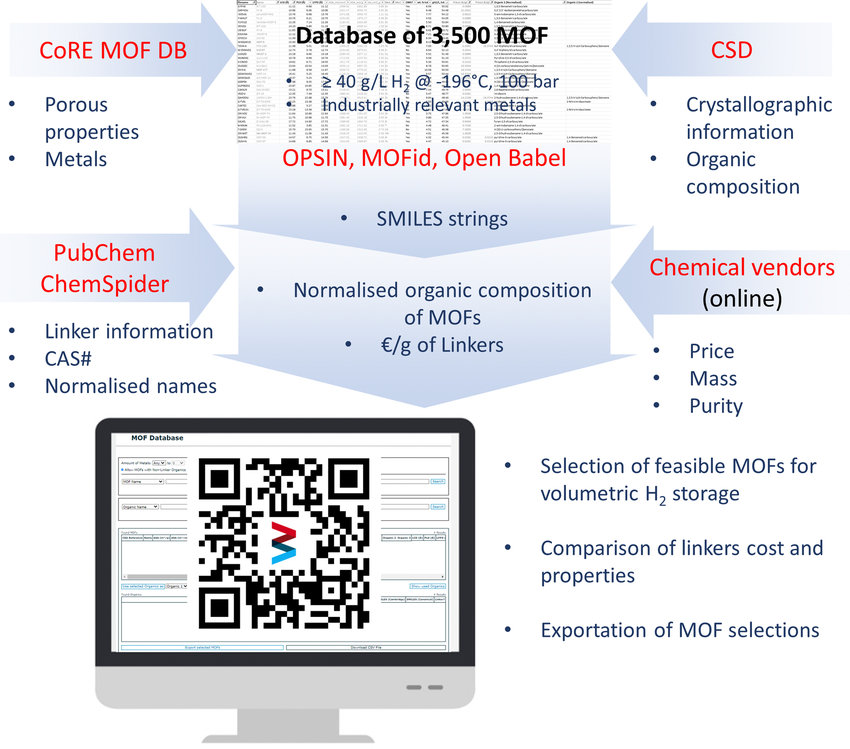
A database to select affordable MOFs for volumetric hydrogen cryoadsorption considering
the cost of their linkers was introduced by CIIAE – Iberian Centre for Research in Energy Storage and Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und –prüfung.
Physical adsorption at cryogenic temperature is a reversible mechanism that can reduce the pressure of conventional compressed gas storage systems. Metal–organic framework (MOF) materials are remarkable candidates due to the combination of high specific surface area and density which, in some cases, provide a high volumetric storage capacity. However, such extensive use of MOF’s for this application requires the selection of affordable structures, easy to produce and made from feasible metallic and organic components. Herein, we introduce a MOF database detailing the crystallographic and porous properties of 3 600 existing MOF’s made from industrially relevant metals and their organic composition. The comparison of the available minimum costs of linkers allowed the creation of a database to select affordable structures with high potential for volumetric hydrogen storage by cryoadsorption, considering their composition based on individual or mixed building blocks. A user interface, available online, facilitates the selection of MOFs based on the properties or names of structure and linkers.
For detailed information read the technical article published in “Royal society of science” about the created database and a description of the database